Every click, scroll, or purchase on a website is shaped by human psychology. well-designed website is not just visually appealing; it also affects behavior, trust, and decision-making. This is where UX psychology plays a crucial role.
In this blog, we’ll explore the psychological principles behind good UX design, and how you can apply them to create websites that not only look great but also convert visitors into loyal customers.
First Impressions & Cognitive Bias
We process visuals faster than words. In fact, it takes just 50 milliseconds for users to form an impression of your site. If the first impression is poor, users often leave and never return.
Good UX taps into this by using:
- Clean layouts
- Balanced white space
- Intuitive navigation:Consistent branding
- Impact: Easy navigation reduces bounce rates and improves time-on-site.
Psychology Principle: Primacy Effect – users remember their first impression the most.
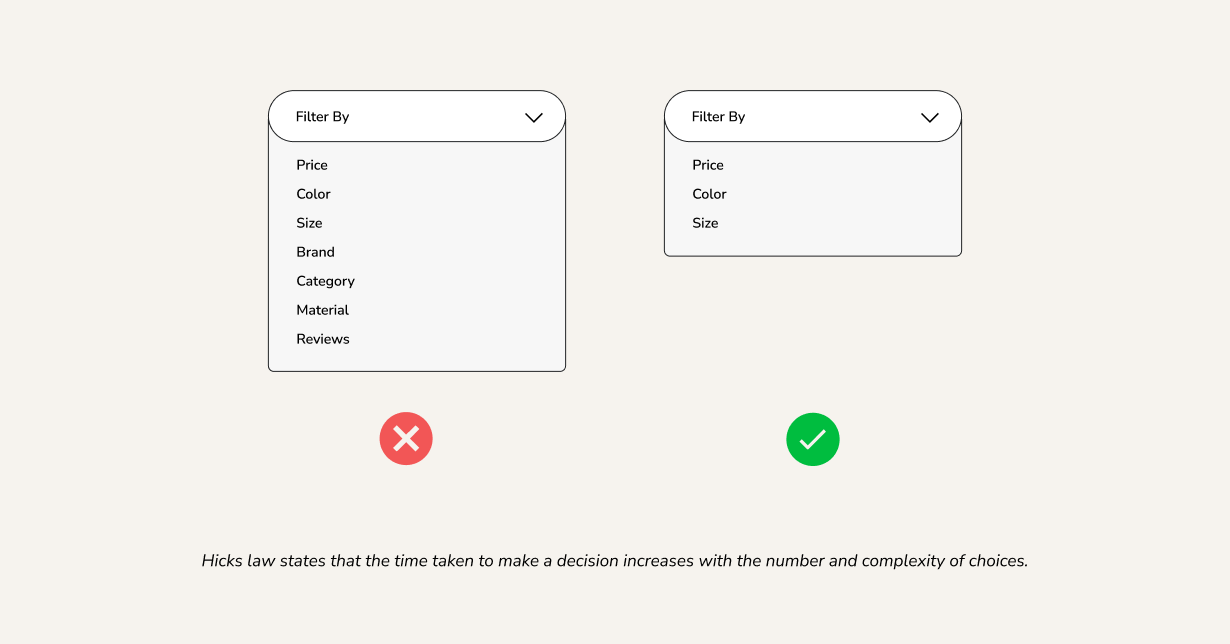
Hick’s Law – The Power of Simplicity
Hick’s Law states: The more choices you give a user, the longer they take to decide. Too many buttons, links, or forms create decision fatigue.
Application in UX:
- Keep menus under 7 items
- Use single, clear CTAs per page
- Avoid unnecessary steps in forms or checkout
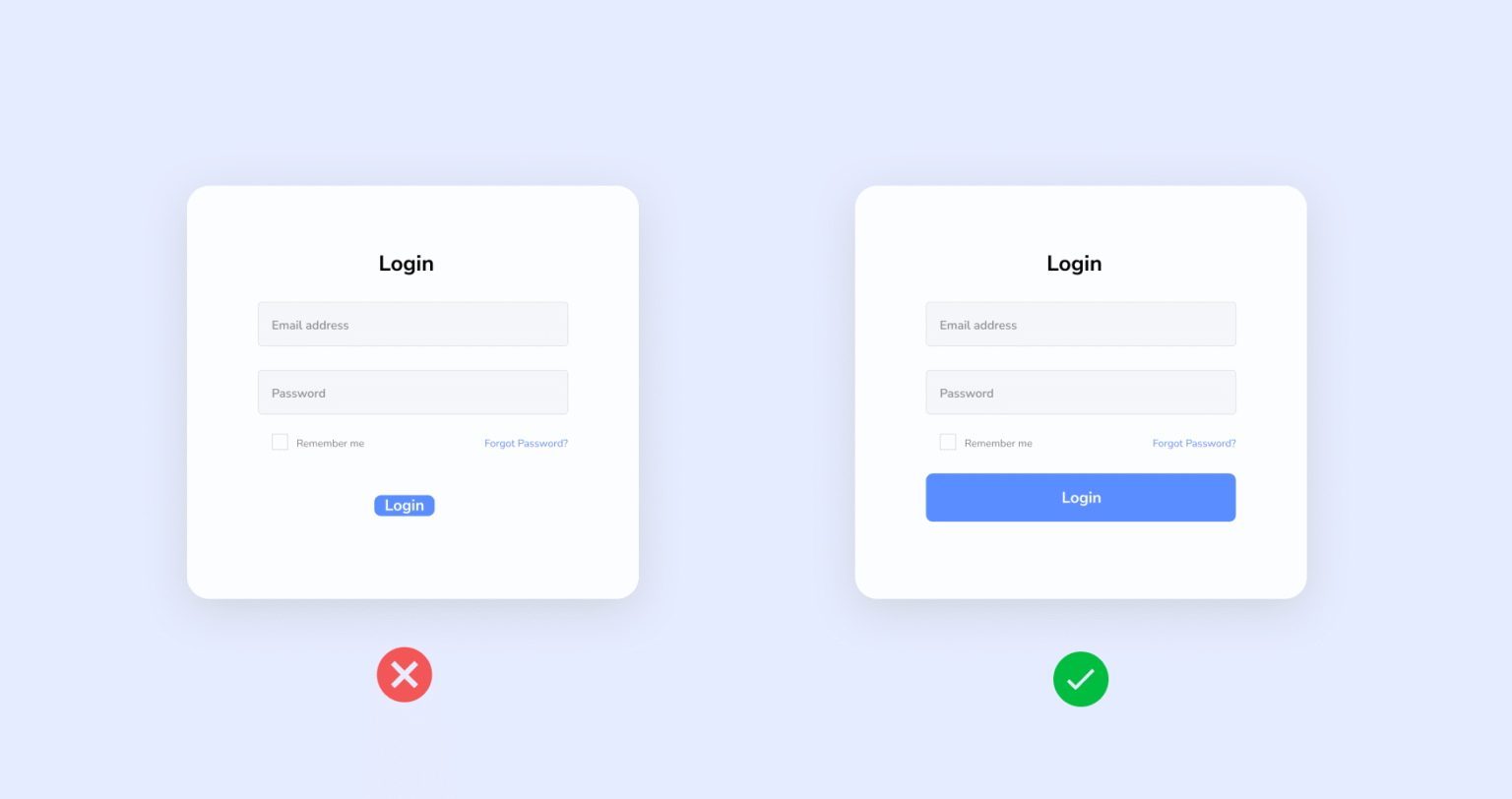
The Principle of Fitts’s Law
Fitts’s Law explains that the time to reach a target (CTA button or link) depends on its size and distance. Smaller, hidden buttons make users frustrated.
- Problem: Walls of text, lack of headings, and bad color contrast.
- Solution: Break content into short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings. Use at least a 16px readable font size and high-contrast text colors.
- Impact: Improves accessibility, engagement, and SEO rankings.
The Psychology of Colors
Colors trigger emotions and associations. For example:
- Blue = Trust & Security (used by banks, healthcare)
- Green = Growth & Positivity (used by eco brands)
- Red = Urgency or Excitement (used in sales/promotions)

Social Proof & Trust Building
Humans are influenced by others’ actions. This is why reviews, testimonials, and social proof are powerful UX elements.
UX examples:
- Add customer reviews below products
- Use star ratings or “verified purchase” tags
- Show case studies, logos of past clients, or real-time usage stats
Psychology Principle: Social Validation – people trust the crowd’s choices.
The Psychology of Cognitive Load
Too much information overwhelms users. A high cognitive load makes websites harder to use.
Reduce cognitive load by:
- Breaking content into smaller sections.
- Using icons and visuals instead of long text.
- Applying progressive disclosure (show info only when needed).
Reciprocity & Micro-Interactions
When you give users something valuable, they feel compelled to return the favor. This principle of reciprocity drives engagement. In UX:- Offer free resources (guides, tools)
- Use micro-interactions (animations, hover states) to make interactions rewarding
- Provide instant feedback (form confirmation messages, progress bars)
Conclusion
Good UX design is not just about aesthetics – it’s about understanding human psychology. By applying principles like Hick’s Law, Fitts’s Law, color psychology and social proof, you can create websites that are intuitive, trustworthy and conversion-friendly.
At uxful.in we design with psychology in mind – ensuring every pixel, button and flow enhances user trust and business growth
👉Want to see how psychology shapes your website’s UX? Book a free UX Audit today